| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 |
| 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 |
| 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
- 이진탐색
- docker
- 티스토리챌린지
- 이분탐색
- 트리
- programmers
- Security
- N과M
- DP
- Java
- 투포인터
- priorityqueue
- Spring
- JPA
- 그리디
- Simulation
- BFS
- Queue
- Stack
- 퀵정렬
- BOJ
- 취준
- CS
- 도커교과서
- 구현
- 오블완
- MySQL
- 백트래킹
- dfs
- 코딩테스트
- Today
- Total
Untitled1.class
Method Security 본문
Spring Security는 Request 수준에서 권한 부여를 모델링하는 것 외에도 method 수준에서도 모델링을 지원한다.
Application에서 @Configuration class에 @EnableMethodSecurity annotation을 추가하거나 XML 설정 파일에 <method-security>를 추가하여 이 기능을 활성화할 수 있다.
그러면 @PreAuthorize, @PostAuthorize, @PreFilter, @PostFilter로 Spring 관리 class나 method에 즉시 주석을 달아 입력 매개변수와 반환 값을 포함한 method 호출을 승인할 수 있다.
How Method Security Works
Spring Security의 method 권한 부여 지원은 다음과 같은 경우에 유용하다:
- 세분화된 권한 부여 로직 추출(예: method 매개변수와 반환 값이 권한 부여 결정에 영향을 미치는 경우)
- Service 계층에서 보안 강화
- HttpSecurity 기반 구성보다 annotation 기반 구성을 스타일적으로 선호
또한 Method Security는 Spring AOP를 사용하여 구축되었으므로 필요에 따라 Spring Security의 기본값을 재정의할 수 있는 모든 표현력을 활용할 수 있다.
Method 권한 부여는 Method 이전 권한 부여와 Method 이후 권한 부여의 조합이다. 다음과 같은 방식으로 annotation이 추가된 Service bean을 생각해 보라:
@Service
public class MyCustomerService{
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('permission:read')")
@PostAuthorize("returnObject.owner == authentication.name")
public Customer readCustomer(String id){ ... }
}
Method Security가 활성화되면 MyCustomerService#readCustomer에 대한 호출은 다음과 같이 보일 수 있다:
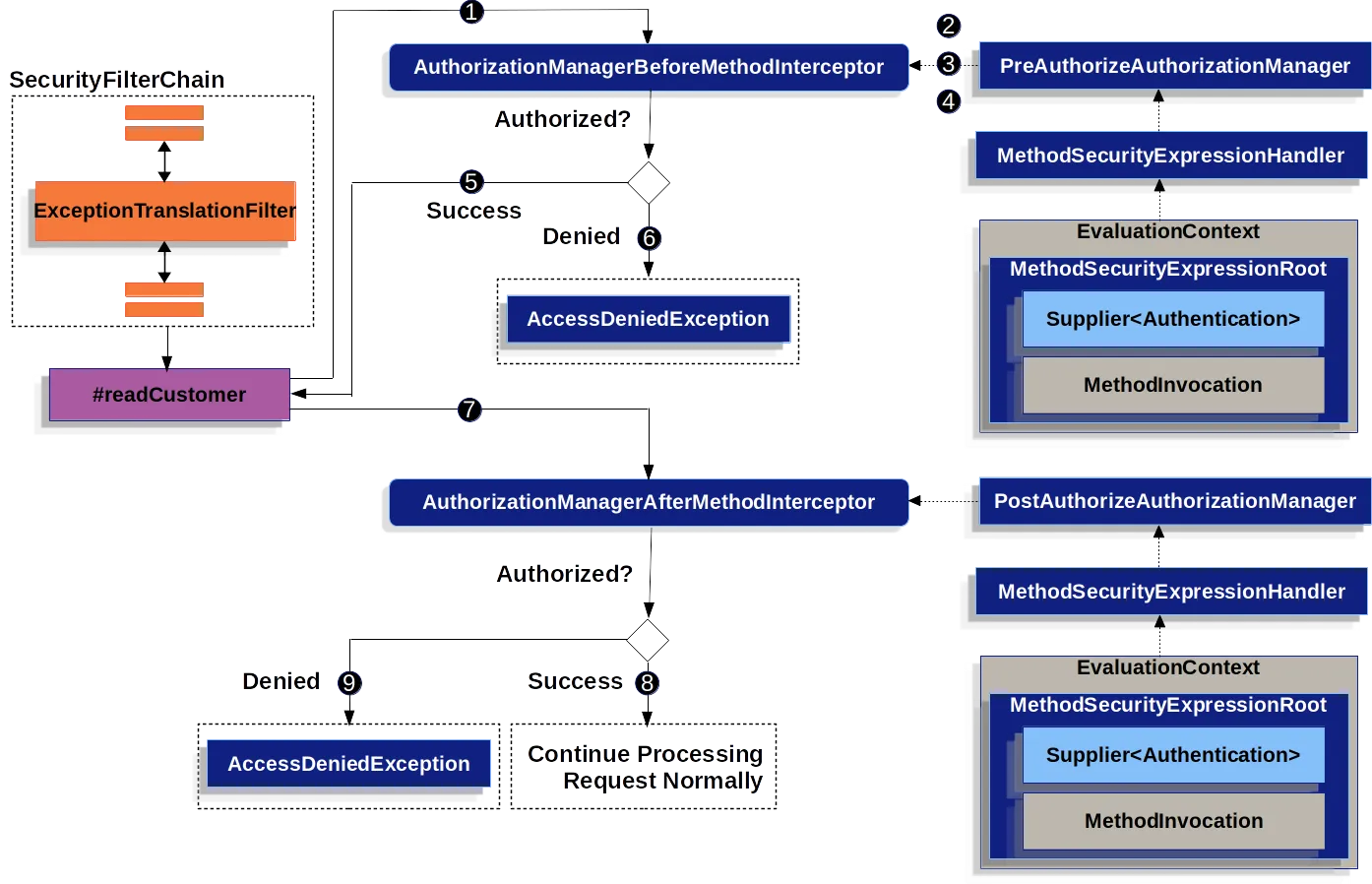
- Spring AOP는 readCustomer에 대한 Proxy Method를 호출한다. Proxy의 다른 Advisor 중에서 @PreAuthorize 포인트 컷과 일치하는 AuthorizationManagerBeforeMethodInterceptor를 호출한다.
- Interceptor는 PreAuthorizeAuthorizationManager#check를 호출한다.
- AuthorizationManager는 MethodSecurityExpressionHandler를 사용하여 annotation의 SpEL 표현식을 parsing하고, Supplier<Authentication>과 MethodInvocation을 포함하는 MethodSecurityExpressionRoot에서 해당 EvaluationContext를 생성한다.
- Interceptor는 이 Context를 사용하여 표현식을 평가한다. 구체적으로, Supplier에서 Authentication을 읽고 권한 컬렉션에 permission:read가 있는지 확인한다.
- 평가가 통과되면 Spring AOP는 해당 method를 호출한다.
- 그렇지 않으면 Interceptor는 AuthorizationDeniedEvent를 발행하고 AccessDeniedException을 발생시킨다. ExceptionTranslationFilter는 이를 포착하여 응답에 403 상태 코드를 반환한다.
- Method가 반환된 후, Spring AOP는 @PostAuthorize 포인트컷과 일치하는 AuthorizationManagerAfterMethodInterceptor를 호출한다. 이 호출은 위와 동일하게 작동하지만 PostAuthorizeAuthorizationManager를 사용한다.
- 평가가 통과되면(이 경우 반환 값이 login한 사용자의 값임) 처리는 정상적으로 진행된다.
- 그렇지 않으면 Interceptor는 AuthorizationDeniedEvent를 발행하고 AccessDeniedException을 발생시킨다. ExceptionTranslationFilter는 이를 포착하여 응답에 403 상태 코드를 반환한다.
Multiple Annotations Are Computed In Series
위에서 설명한 것처럼, Method 호출에 여러 개의 Method Security annotation이 포함된 경우 각 annotation은 한 번에 하나씩 처리된다. 즉, 이러한 annotation들은 집합적으로 “anded”된 것으로 간주될 수 있다. 다시 말해, 호출이 승인되려면 모든 annotation 검사가 승인을 통과해야 한다.
Repeated Annotations Are Not Supported
하지만 동일한 Method에 동일한 annotation을 반복하는 것은 지원되지 않는다. 예를 들어, 동일한 Method에 @PreAuthorize를 두 번 적용할 수 없다.
대신 SpEL의 bool 지원이나 별도의 bean에 위임하는 기능을 사용하라.
Each Annotation Has Its Own Pointcut
각 annotation에는 Method와 해당 annotation을 둘러싼 class부터 시작하여 전체 객체 계층 구조에서 해당 annotation이나 meta-annotation 대응 항목을 찾는 자체 포인트컷 instance가 있다.
Each Annotation Has Its Own Method Interceptor
각 annotation에는 자체적인 Method Interceptor가 있다. 이는 구성 가능성을 높이기 위한 것이다. 예를 들어, 필요한 경우 Spring Security 기본값을 비활성화하고 @PostAuthorize Method Interceptor만 게시할 수 있다.
Method Interceptor는 다음과 같다:
- @PreAuthorize: AuthorizationManagerBeforeMethodInterceptor#preAuthorize를 사용하고, 이는 다시 PreAuthorizeAuthorizationManager를 사용한다.
- @PostAuthorize: AuthorizationManagerAfterMethodInterceptor#postAuthorize를 사용하고, 이는 다시 PostAuthorizeAuthorizationManager를 사용한다.
- @PreFilter: PreFilterAuthorizationMethodInterceptor를 사용한다.
- @PostFilter: PostFilterAuthorizationMethodInterceptor를 사용한다.
- @Secured: AuthorizationManagerBeforeMethodInterceptor#secured를 사용하고, 이는 다시 SecuredAuthorizationManager를 사용한다. (@PreAuthorize 사용 권장)
- JSR-250 annotation: AuthorizationManagerBeforeMethodInterceptor#jsr250을 사용하고, 이는 다시 Jsr250AuthorizationManager를 사용한다. (@PreAuthorize 사용 권장)
일반적으로 @EnableMethodSecurity를 추가하면 Spring Security에서 Interceptor가 게시하는 내용을 대표하는 목록은 다음과 같다:
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
static Advisor preAuthorizeMethodInterceptor() {
return AuthorizationManagerBeforeMethodInterceptor.preAuthorize();
}
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
static Advisor postAuthorizeMethodInterceptor() {
return AuthorizationManagerAfterMethodInterceptor.postAuthorize();
}
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
static Advisor preFilterMethodInterceptor() {
return AuthorizationManagerBeforeMethodInterceptor.preFilter();
}
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
static Advisor postFilterMethodInterceptor() {
return AuthorizationManagerAfterMethodInterceptor.postFilter();
}
Comparing Request-level vs Method-level Authorization
요청 수준 메서드 수준
| 권한 유형 | 거친 | 세밀한 |
| 구성 위치 | config class에서 선언 | method 선언에 |
| 구성 스타일 | DSL | Annotation |
| 권한 정의 | 프로그래밍 방식 | SpEL |
Authorizing with Annotations
Spring Security가 Method 수준 권한 부여 지원을 활성화하는 주요 방법은 Method, class 및 interface에 추가할 수 있는 annotation을 통해서이다.
Authorizing Method Invocation with @PreAuthorize
Method Security가 활성화된 경우 다음과 같이 @PreAuthorize annotation으로 Method에 주석을 달 수 있다:
@Component
public class BankService {
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')")
public Account readAccount(Long id) {
// ... is only invoked if the `Authentication` has the `ROLE_ADMIN` authority
}
}
이는 제공된 표현식 hasRole(’ADMIN’)이 통과하는 경우에만 해당 Method를 호출할 수 있음을 나타낸다.
그런 다음, 다음과 같이 class를 Test하여 권한 부여 규칙이 적용되는지 확인할 수 있다:
@Autowired
BankService bankService;
@WithMockUser(roles="ADMIN")
@Test
void readAccountWithAdminRoleThenInvokes() {
Account account = this.bankService.readAccount("12345678");
// ... assertions
}
@WithMockUser(roles="WRONG")
@Test
void readAccountWithWrongRoleThenAccessDenied() {
assertThatExceptionOfType(AccessDeniedException.class).isThrownBy(
() -> this.bankService.readAccount("12345678"));
}
Authorization Method Results with @PostAuthorize
Method Security가 활성화된 경우 다음과 같이 @PostAuthorize annotation으로 Method에 주석을 달 수 있다:
@Component
public class BankService {
@PostAuthorize("returnObject.owner == authentication.name")
public Account readAccount(Long id) {
// ... is only returned if the `Account` belongs to the logged in user
}
}
이는 제공된 표현식 returnObject.owner == authentication.name이 통과하는 경우에만 Method가 값을 반환할 수 있음을 나타낸다. returnObject는 반환될 Account 객체를 나타낸다.
그런 다음 class를 Test하여 권한 부여 규칙이 적용되는지 확인할 수 있다:
@Autowired
BankService bankService;
@WithMockUser(username="owner")
@Test
void readAccountWhenOwnedThenReturns() {
Account account = this.bankService.readAccount("12345678");
// ... assertions
}
@WithMockUser(username="wrong")
@Test
void readAccountWhenNotOwnedThenAccessDenied() {
assertThatExceptionOfType(AccessDeniedException.class).isThrownBy(
() -> this.bankService.readAccount("12345678"));
}
@PostAuthorize는 특히 안전하지 않은 직접 객체 참조(Insecure Direct Object Reference)를 방어할 때 유용하다. 실제로 다음과 같은 meta-annotation으로 정의할 수 있다:
@Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@PostAuthorize("returnObject.owner == authentication.name")
public @interface RequireOwnership {}
대신 다음과 같은 방법으로 Service에 주석을 달 수 있다:
@Component
public class BankService {
@RequireOwnership
public Account readAccount(Long id) {
// ... is only returned if the `Account` belongs to the logged in user
}
}
결과적으로 위 Method는 소유자 속성이 login한 사용자 이름과 일치하는 경우에만 계정을 반환한다. 그렇지 않으면 Spring Security는 AccessDeniedException을 발생시키고 403 상태 코드를 반환한다.
Filtering Method Parameters with @PreFilter
Method Security가 활성화된 경우 다음과 같이 @PreFilter annotation으로 Method에 주석을 달 수 있다:
@Component
public class BankService {
@PreFilter("filterObject.owner == authentication.name")
public Collection<Account> updateAccounts(Account... accounts) {
// ... `accounts` will only contain the accounts owned by the logged-in user
return updated;
}
}
이는 filterObject.owner == authentication.name 표현식이 실패하는 계정의 모든 값을 필터링하기 위한 것이다. filterObject는 accounts의 각 계정을 나타내며 각 계정을 테스트하는 데 사용된다.
그런 다음, 다음과 같은 방법으로 class를 Test하여 권한 부여 규칙이 적용되는지 확인할 수 있다:
@Autowired
BankService bankService;
@WithMockUser(username="owner")
@Test
void updateAccountsWhenOwnedThenReturns() {
Account ownedBy = ...
Account notOwnedBy = ...
Collection<Account> updated = this.bankService.updateAccounts(ownedBy, notOwnedBy);
assertThat(updated).containsOnly(ownedBy);
}
Filtering Method Parameters with @PostFilter
Method Security가 활성화된 경우 다음과 같이 @PostFilter annotation으로 Method에 주석을 달 수 있다:
@Component
public class BankService {
@PostFilter("filterObject.owner == authentication.name")
public Collection<Account> readAccounts(String... ids) {
// ... the return value will be filtered to only contain the accounts owned by the logged-in user
return accounts;
}
}
이는 filterObject.owner == authentication.name 표현식이 실패하는 경우 반환 값에서 모든 값을 필터링하기 위한 것이다. filterObject는 accounts의 각 계정을 나타내며 각 계정을 테스트하는 데 사용된다.
그런 다음, 다음과 같은 방법으로 class를 Test하여 권한 부여 규칙이 적용되는지 확인할 수 있다:
@Autowired
BankService bankService;
@WithMockUser(username="owner")
@Test
void readAccountsWhenOwnedThenReturns() {
Collection<Account> accounts = this.bankService.updateAccounts("owner", "not-owner");
assertThat(accounts).hasSize(1);
assertThat(accounts.get(0).getOwner()).isEqualTo("owner");
}
Using Meta Annotations
Method Security는 Meta Annotation을 지원한다. 즉, 어떤 Annotation이든 가져와서 Application별 용례에 따라 가독성을 향상시킬 수 있다.
예를 들어, @PreAuthorize(”hasRole(’ADMIN’)”)를 다음과 같이 @IsAdmin으로 간소화할 수 있다:
@Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')")
public @interface IsAdmin {}
결과적으로 보안된 Method에서 다음을 수행할 수 있다:
@Component
public class BankService {
@IsAdmin
public Account readAccount(Long id) {
// ... is only returned if the `Account` belongs to the logged in user
}
}
Templating Meta-Annotation Expressions
또한, 훨씬 더 강력한 Annotation 정의가 가능한 Meta Annotation 템플릿을 사용하도록 선택할 수도 있다.
먼저, 다음 bean을 게시합니다:
@Bean
static AnnotationTemplateExpressionDefaults templateExpressionDefaults() {
return new AnnotationTemplateExpressionDefaults();
}
이제 @IsAdmin 대신 다음과 같이 @HasRole과 같이 더 강력한 것을 만들 수 있습니다:
@Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('{value}')")
public @interface HasRole {
String value();
}
결과적으로 보안된 Method에서 다음을 수행할 수 있다:
@Component
public class BankService {
@HasRole("ADMIN")
public Account readAccount(Long id) {
// ... is only returned if the `Account` belongs to the logged in user
}
}
이 방법은 Method 변수와 모든 Annotation 유형에서도 작동하지만, 결과 SpEL 표현식이 올바르도록 따옴표를 올바르게 사용하는 것이 중요하다.
예를 들어, 다음의 @HasAnyRole Annotation을 생각해 보라:
@Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@PreAuthorize("hasAnyRole({roles})")
public @interface HasAnyRole {
String[] roles();
}
그런 경우에는, 표현식에서 따옴표를 사용하지 말고 대신 다음과 같이 매개변수 값에서 따옴표를 사용해야 한다는 것을 알 수 있다:
@Component
public class BankService {
@HasAnyRole(roles = { "'USER'", "'ADMIN'" })
public Account readAccount(Long id) {
// ... is only returned if the `Account` belongs to the logged in user
}
}
참조
'공부 > Spring Security' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Authorize HttpServletRequests (0) | 2025.05.13 |
|---|---|
| Username/Password Authentication (0) | 2025.05.13 |
| Spring Security Authorization Architecture (0) | 2025.05.13 |
| Spring Security Authentication Architecture (0) | 2025.05.13 |
| Spring Security Servlet Applications Architecture (0) | 2025.05.12 |




